Experience 50 Cases of Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Underwent Ramstids' surgery in Karbala
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/M229Abstract
Background: Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction in infants. There is a paucity of published data regarding this condition in our setting. This study describes the clinical presentation, mode of treatment, and outcome of treatment for this disease, and identifies factors responsible for the poor outcome in these patients.
Methods: This was a descriptive retrospective study of infants with Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis admitted to hospitals in Karbala between January 1, 2020, and October 24, 2024 (50 cases, 40 males, 10 females).
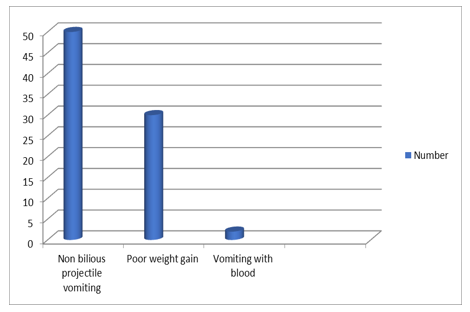
Results: electrolyte disturbance, including Hyponatremia, hypochloremia, Hypokalemia, and Metabolic alkalosis. Division of case number by age, including (1-2 weeks is 2), (2-6 weeks is 40), and (older than 6 weeks is 8). Clinical features presentation number, including (non-bilious projectile vomiting = 50, poor weight gain =30, and vomiting with blood = 2). Post-operative complications including surgical site infection = 5 cases, incisional hernia = 1 case, post-operative emesis = 10 cases, and death = zero.
Conclusion: Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is the predominant cause of gastric outlet obstruction in newborns in our context. A guideline should be established to rectify fluid and electrolyte imbalances post-diagnosis to reduce perioperative hospital duration. Postoperatively, these patients require meticulous management in the pediatric ward, particularly during the first postoperative phase. Additional research is required in this domain to enhance the management of infants with infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
References
Ramstedt C. Zur operation der angeborenen pylorus-stenose. Med Klin. 1912; 8:1702–5.
Hirschsprung H. Falle von angeborener pyloric stenose. Jb Kinderheik. 1888; 27:61.
To T, Wajja A, Wales PW, Langer JC. Population demographic indicators associated with incidence of pyloric stenosis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005; 159:520. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.159.6.520
Mullassery D, Perry D, Goyal A, Jesudason EC, Losty PD. Surgical practice for infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in the United Kingdom and Ireland—a survey of members of the British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:1227–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.12.075
Roldan-Valadez E, Solorzano-Morales S, Osorio-Peralta S. Imaging diagnosis of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: report of a case and review of the literature. Rev Gastroenteral Mex. 2007; 72:126–32.
Touloukian RJ, Higgins E. The spectrum of serum electrolytes in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1983; 18:394. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3468(83)80188-2
Nmadu PT. Alterations in serum electrolytes in congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: a study in Nigerian children. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1992; 12:169. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02724936.1992.11747564
Hernanz-Schulman M. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Radiology. 2003; 227:319–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2272011329
Aspelund G, Langer JC. Current management of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2007; 16:27–33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2006.10.004
Nasr A, Ein SH. Postoperative pyloric stenosis in the newborn: a forgotten problem. J Pediatr Surg. 2007; 42:1409–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.03.043
Mandell GA, Wolfson PJ, Adkins ES, Caro PA, Cassell I, Finkelstein MS, Grissom LE, Gross GW, Harcke HT, Katz AL, Murphy SG, Noseworthy J, Schwartz MZ. Cost-effective imaging approach to the nonbilious vomiting infant. Pediatrics. 1999; 103:1198. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.103.6.1198
Applegate MS, Druschel CM. The epidemiology of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in New York State: 1983 to 1990. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995;149(10):1123‐1129. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.1995.02170230077011
Ramstedt C. Zur operation der angeborenen pylorus-stenose. Med Klin. 1912; 8:1702–5.
Hirschsprung H. Falle von angeborener pyloric stenose. Jb Kinderheik. 1888; 27:61.
Kaye P. Acquired pyloric stenosis resulting in hypokalaemic, hyperchloraemic normal anion gap metabolic acidosis. Persistent vomiting in an adult: cause and effect. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Jan 17;2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-222800
Roldan-Valadez E, Solorzano-Morales S, Osorio-Peralta S. Imaging diagnosis of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: report of a case and review of the literature. Rev Gastroenteral Mex. 2007; 72:126–32.
Bašković M, Župančić B, Lesjak N, Vukasović I. Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis - Five-Year Retrospective Analysis. Acta Med Croatica. 2016 Apr;70(2):103-6.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Academic International Journal of Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








