Trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) As A Prognostic and Pathogenic Factor in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma in Iraqi Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/M314Keywords:
Prostate Cancer, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Prostatic Adenocarcinoma, Trefoil Factor 3 (TFF3), Tumor BiomarkerAbstract
Background: The prostate gland has a high rate of benign and malignant disease, including “benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)” and prostatic adenocarcinoma. BPH occurs in as many as 75% of males by the eighth decade of life. “Prostate cancer” is the second most common cancer in the world, and in Iraq, it is the third most common cancer after lung and colorectal cancers. “Trefoil factor 3 (TFF3)” is a member of the trefoil factor family, which has been associated with epithelial repair and tumorigenesis. TFF3 promotes a cancerous state by increasing cell migration, invasion, and the formation of the tumor microenvironment, and by inhibiting apoptosis, likely through the activation of a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway.
Aim: This study aimed to evaluate TFF3 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma versus BPH and to assess its correlation with pathological features, including age, preoperative PSA level, Gleason grade, perineural, and lymphovascular invasion.
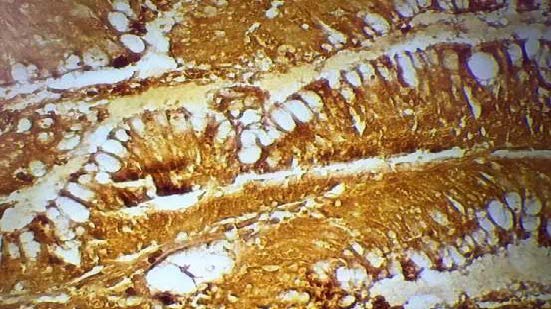
Method: An examination of sixty formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded prostatic tissue blocks was performed: 30 “benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)” and 30 prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical staining with anti-TFF3 monoclonal antibody were performed on each block. TFF3 expression was qualitatively evaluated under light microscopy and correlated with computer-derived clinicopathologic characteristics.
Results: TFF3 expression was demonstrated in 93.3% of cases of prostatic adenocarcinoma and was expressed in only 20% of BPH cases. A highly statistically significant correlation was observed between TFF3 expression and Gleason grade (p = 0.00004) and with preoperative PSA (p = 0.000012). There was no statistically significant correlation with age, perineural, or lymphovascular invasion. TFF3 has a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 80% as a diagnostic marker.
Conclusion: TFF3 is significantly overexpressed in prostatic adenocarcinoma compared to BPH, particularly in high-grade tumors, supporting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-49. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Wang L, Lu B, He M, Wang Y, Wang Z, Du L. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Global Status and Temporal Trends in 89 Countries From 2000 to 2019. Front Public Health. 2022;10:811044. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.811044
Environment RoIMoHa. Iraqi Cancer Registry 2020 Baghdad: Ministry of Health; 2020 [Available from: https://moh.gov.iq/upload/2991322580.pdf.
Rawla P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J Oncol. 2019;10(2):63-89. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon1191
Giri VN, Beebe-Dimmer JL. Familial prostate cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43(5):560-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.08.001
PeaceHealth M, a Bill P. Genetics of Prostate Cancer (PDQ®): Genetics-Health Professional Information [NCI].
Thompson IM, Pauler DK, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Parnes HL, et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level≤ 4.0 ng per milliliter. New England Journal of Medicine. 2004;350(22):2239-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa031918
Humphrey PA. Gleason grading and prognostic factors in carcinoma of the prostate. Modern pathology. 2004;17(3):292-306. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800054
Berney DM, Beltran L, Fisher G, North BV, Greenberg D, Møller H, et al. Validation of a contemporary prostate cancer grading system using prostate cancer death as outcome. British journal of cancer. 2016;114(10):1078-83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.86
McVary KT, Roehrborn CG, Avins AL, Barry MJ, Bruskewitz RC, Donnell RF, et al. Update on AUA guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Journal of urology. 2011;185(5):1793-803. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.01.074
Roehrborn C. Pathology of benign prostatic hyperplasia. International journal of impotence research. 2008;20(3):S11-S8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2008.55
Hoffmann W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and their diverse molecular functions in mucus barrier protection and more: changing the paradigm. International journal of molecular sciences. 2020;21(12):4535. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124535
Braga Emidio N, Brierley SM, Schroeder CI, Muttenthaler M. Structure, function, and therapeutic potential of the trefoil factor family in the gastrointestinal tract. ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science. 2020;3(4):583-97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.0c00023
Lin X, Zhang H, Dai J, Zhang W, Zhang J, Xue G, et al. TFF3 Contributes to Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells via the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway. J Cancer. 2018;9(23):4430-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.24361
Liu J, Kim SY, Shin S, Jung SH, Yim SH, Lee JY, et al. Overexpression of TFF3 is involved in prostate carcinogenesis via blocking mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(8):1-11.
Faith DA, Isaacs WB, Morgan JD, Fedor HL, Hicks JL, Mangold LA, et al. Trefoil factor 3 overexpression in prostatic carcinoma: prognostic importance using tissue microarrays. Prostate. 2004;61(3):215-27.
Liu J, Kim SY, Shin S, Jung S-H, Yim S-H, Lee JY, et al. Overexpression of TFF3 is involved in prostate carcinogenesis via blocking mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Experimental & molecular medicine. 2018;50(8):1-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0137-7
Terry S, Nicolaiew N, Basset V, Semprez F, Soyeux P, Maillé P, et al. Clinical value of ERG, TFF3, and SPINK1 for molecular subtyping of prostate cancer. Cancer. 2015;121(9):1422-30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29233
Yang Y, Lin Z, Lin Q, Bei W, Guo J. Pathological and therapeutic roles of bioactive peptide trefoil factor 3 in diverse diseases: recent progress and perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(1):62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04504-6
Bujak M, Bujak IT, Sobočanec S, Mihalj M, Novak S, Ćosić A, et al. Trefoil factor 3 deficiency affects liver lipid metabolism. Cellular physiology and biochemistry. 2018;47(2):827-41. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000490039
Šešelja K, Bazina I, Welss J, Schicht M, Paulsen F, Bijelić N, et al. Effect of Tff3 deficiency and ER stress in the liver. International journal of molecular sciences. 2019;20(18):4389. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184389
Garraway IP, Seligson D, Said J, Horvath S, Reiter RE. Trefoil factor 3 is overexpressed in human prostate cancer. Prostate. 2004;61(3):209-14.
Vestergaard EM, Borre M, Poulsen SS, Nexø E, Tørring N. Plasma levels of trefoil factors are increased in patients with advanced prostate cancer. Clinical cancer research. 2006;12(3):807-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1545
Lindberg MR. Diagnostic Pathology: Normal Histology-E-Book: Diagnostic Pathology: Normal Histology-E-Book: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2017.
Timofte AD, Giuşcă SE, Lozneanu L, Manole MB, Prutianu I, Gafton B, et al. HOXB13 and TFF3 can contribute to the prognostic stratification of prostate adenocarcinoma. Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology. 2021;62(1):41. DOI: https://doi.org/10.47162/RJME.62.1.04
Garraway IP, Seligson D, Said J, Horvath S, Reiter RE. Trefoil factor 3 is overexpressed in human prostate cancer. The Prostate. 2004;61(3):209-14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20096
Noiwan S, Rattanarapee S. Mucin production in prostatic adenocarcinoma: a retrospective study of 190 radical prostatectomy and/or core biopsy specimens in department of pathology, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand= Chotmaihet Thangphaet. 2011;94(2):224-30.
Liu M, Jin R. Expressions of TFF1 and TFF3 in prostate cancer and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and their clinical significance. Zhonghua nan ke xue= National Journal of Andrology. 2015;21(4):315-9.
Yusufu A, Shayimu P, Tuerdi R, Fang C, Wang F, Wang H. TFF3 and TFF1 expression levels are elevated in colorectal cancer and promote the malignant behavior of colon cancer by activating the EMT process. International journal of oncology. 2019;55(4):789-804. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4854
Faith DA, Isaacs WB, Morgan JD, Fedor HL, Hicks JL, Mangold LA, et al. Trefoil factor 3 overexpression in prostatic carcinoma: prognostic importance using tissue microarrays. The Prostate. 2004;61(3):215-27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20095
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








