Epidemiological Study of Brucella abortus Infection in Wasit Province
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/M311Keywords:
Brucellosis, Brucella abortus, Zoonotic disease, public health, Epidemiology.Abstract
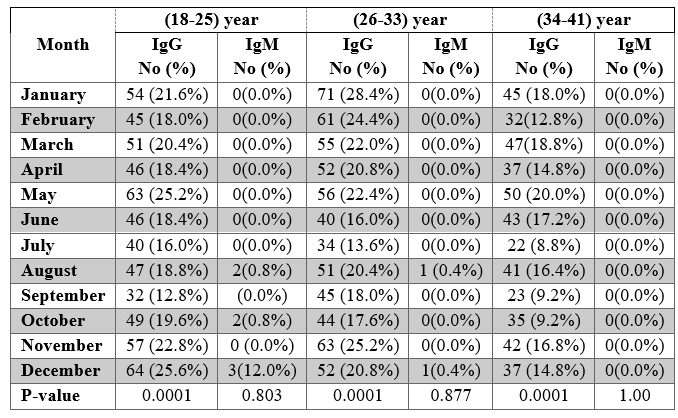
Brucellosis, caused by Brucella abortus, remains a significant public health challenge in many regions, including Wasit Province, Iraq. This study analyzed the infection's seasonal trends and age-specific prevalence to understand its epidemiology better. Data from 2022 and 2023 indicated peak IgG positivity in January, May, and June, which were in line with the seasonality of agriculture. Interestingly, IgM positivity appeared sporadically, indicating limited acute infection or a lag in diagnosis. Age group 18-41 years had higher IgG rates, which pointed to occupational risk for subjects dealing with livestock. Findings here indicate the need for targeted interventions like improved veterinary services, public awareness campaigns, and vaccination programs on the persistent risk of zoonotic transmission. Such measures would focus on lessening the burden of brucellosis and protecting human and animal health in the region.
References
Shoukat S, Wani H, Ali U, Para PA, Ara S, Ganguly S. Brucellosis: A current review update on zoonosis. 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5958/0973-9149.2017.00009.0
Pal M, Kerorsa GB, Desalegn C, Kandi V. Human and animal brucellosis: a comprehensive review of biology, pathogenesis, epidemiology, risk factors, clinical signs, laboratory diagnosis. American Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2020;8(4):118-26.
Newell DG, Koopmans M, Verhoef L, Duizer E, Aidara-Kane A, Sprong H, et al. Food-borne diseases—the challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. International journal of food microbiology. 2010;139:S3-S15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.01.021
Laine CG, Johnson VE, Scott HM, Arenas-Gamboa AM. Global estimate of human brucellosis incidence. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2023;29(9):1789. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2909.230052
Al-Bayaa YJ. Epidemiology of Human Brucellosis among Populations in Iraq's Provinces in 2015. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine Baghdad. 2017;59(2):165-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.592130
Alqaseer K, Al-Khafajy A, Almkhadhree E. Serological and molecular detection of human brucellosis in rural areas in Wasit Province, Iraq. Archives of Razi Institute. 2023;78(1):369.
Yagupsky P, Morata P, Colmenero JD. Laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis. Clinical microbiology reviews. 2019;33(1):10.1128/cmr. 00073-19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00073-19
Barbuddhe S, Unni V, Vergis J, Rawool D. brucellosis (Brucella abortus). 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/cabicompendium.90736
Mosimane I. The prevalence of bacterial contamination with reference to Brucella abortus in slaughtered carcasses in selected abattoirs in the North West Province, South Africa: North-West University (South Africa); 2019.
Salih HMS. Brucellosis in Iraq: Epidemiology, present status, and Challenges in controlling the disease: Kansas State University; 2010.
Al-Mashhadany D. The significance of milk ring test for identifying Brucella antibodies in cows and buffaloes' raw milk at Erbil governorate, Kurdistan region, Iraq. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33899/ijvs.2019.163085
Ilyas M, Harpke M, Wareth G. Brucellosis in Iraq: A comprehensive overview of public health and agricultural challenges. Ger. J Microbiol. 2024;4(3):10-20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.51585/gjm.2024.3.0039
Lagadinou M, Mplani V, Velissaris D, Davlouros P, Marangos M. Myocarditis caused by Brucella melitensis in the absence of endocarditis: case report and review of the literature. Case reports in medicine. 2019;2019(1):3701016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3701016
Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM, Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SMR. Osteoarticular manifestations of human brucellosis: a review. World journal of orthopedics. 2019;10(2):54. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v10.i2.54
FAO, editor Brucella melitensis in Eurasia and the Middle East. FAO Technical Meeting in Collaboration with WHO and OIE; 2010.
Jabary OM, Al-Samarraee IA. Detection of Brucella antibodies of sheep and goats by using two serological tests in Al-Sulaimanya governorate. Iraqi J Vet Med. 2015;39:32-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.30539/iraqijvm.v39i2.174
Turgay Ö, Ahmed C. The prevalence of brucellosis in goat and sheep milk samples in Duhok District. 2016.
Mustafa AH, Khaleel HA, Lami F. Human brucellosis in Iraq: spatiotemporal data analysis from 2007-2018. JMIRx Med. 2024;5:e54611. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2196/54611
Musallam I, Abo-Shehada M, Hegazy Y, Holt H, Guitian F. Systematic review of brucellosis in the Middle East: disease frequency in ruminants and humans and risk factors for human infection. Epidemiology & Infection. 2016;144(4):671-85. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268815002575
Assafi MS, Allu MA, Abdulrahman IS, Al-Berfkani MI. The seroprevalence of human brucellosis in different age groups patients and other associated risk factors in Duhok, Iraq. Innovaciencia. 2019;7(2). DOI: https://doi.org/10.15649/2346075X.479
Jokar M, Rahmanian V, Golestani N, Raziee Y, Farhoodi M. The global seroprevalence of equine brucellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on publications from 1990 to 2022. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science. 2023;123:104227. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jevs.2023.104227
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








